Business analysis is a fascinating subject.
As business analysts, we need to understand enterprises very well. However, when we look at different frameworks available for business analysis, they seem to be somewhat limited in their scope. Some of them are good in strategic thinking (like SWOT), some of them are good in tactical thinking (Business model canvas, SIPOC, VSM etc.), but there are no frameworks which give us an idea which covers both strategy and tactical aspects.
Business analysis canvas is an attempt to fulfill this need. In this, we are going to start with strategy and go down to the operational level.
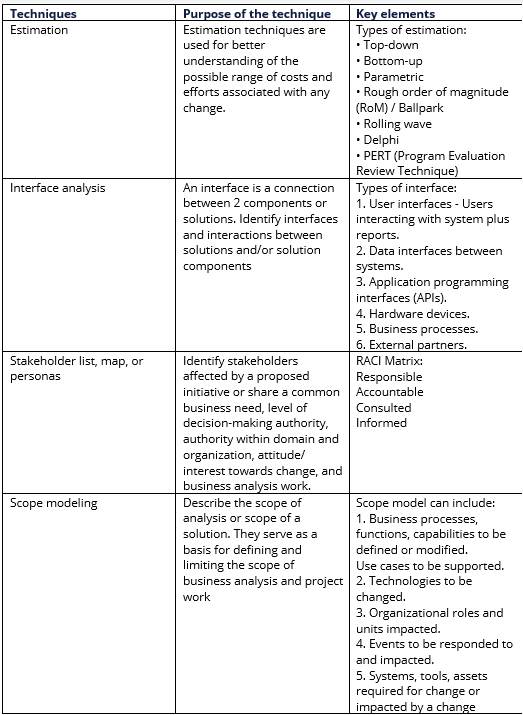
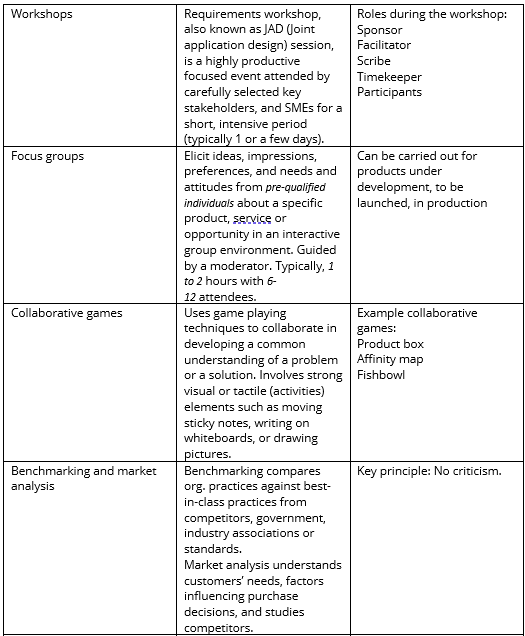
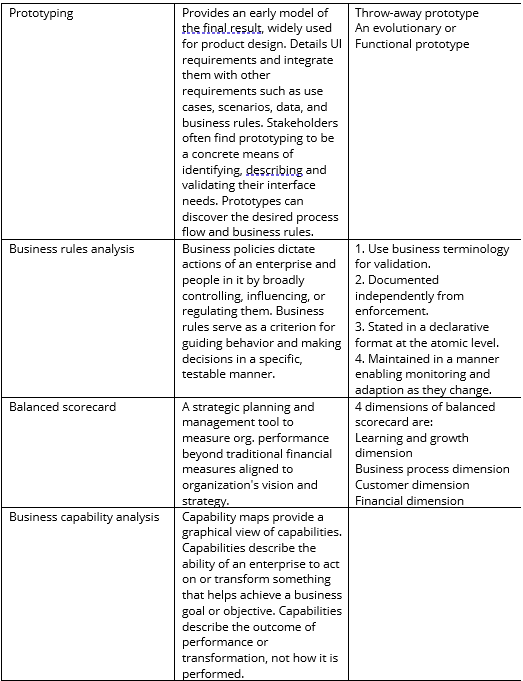
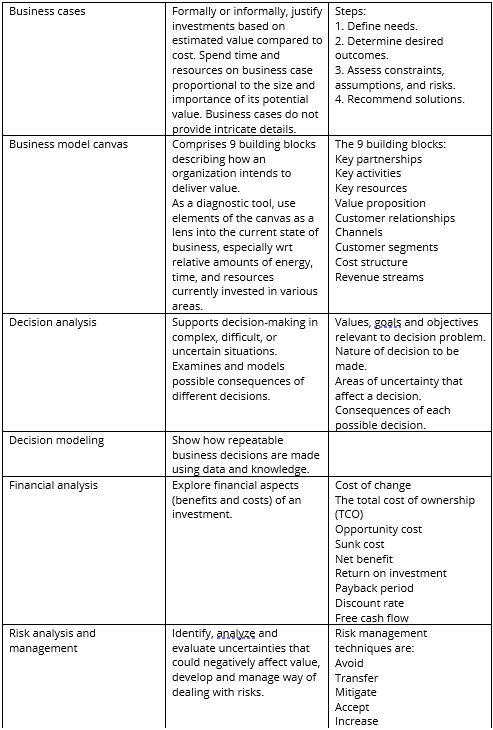
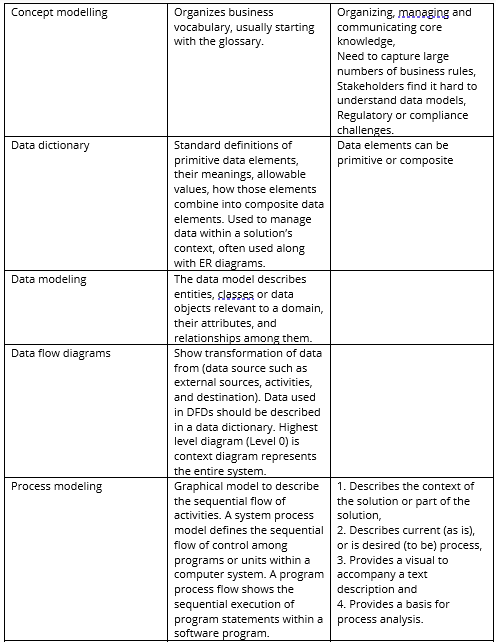
Essentially it has 10 core elements and each core element, of course, has sub-elements which we need to understand. Here, we shall go through one by one:
1. Vision / Goal / Objectives
2. External environment
3. Internal environment
4. Strategies
5. Customer management
6. Cost management
7. Stakeholder management
8. Product and services management
9. Risk management
10. Resources
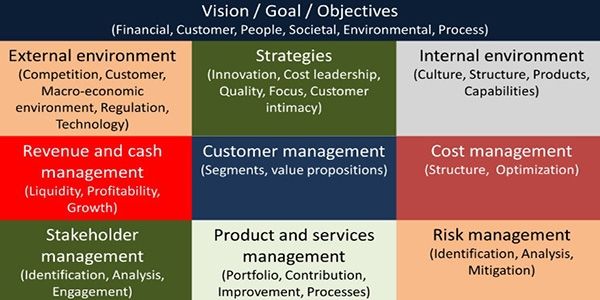
1. Vision / Goal / Objectives
(Financial, Customer, People, Societal, Environmental, Process)
Vision / goal / objectives are essential for any organization to have long-term sustainable growth. Without a vision, it may be difficult for an enterprise to maintain focus. Organizations that do not develop a proper vision or goal usually underperform in the long term.
The organization can set goals and objectives with respect to various aspects such as financial, customer, people, societal, environmental, process etc.
2. External environment
(Competition, Customer, Macroeconomic environment, Regulation, Technology)
The second key element that business analysts must pay attention to is what is happening in the external environment. All businesses operate within an economic environment, which is changing constantly.
Environment essentially comprises of factors like competitors, customers, macroeconomic factors, regulation, and technology.This offers tremendous opportunity, as well as posing threats to the organization. So business analysts must figure out what is happening in the external environment, and how can the organization take benefit of the changes in the environment, or protect itself from the threats arising from the external environment.
3. Internal environment
(Culture, Structure, Products, Capabilities)
After external environment, the next element that business analysts must pay close attention to is the internal environment of the organization. Some the key factors that we look for in an internal environment are the culture of the organization, structure of the organization, the products that the organization has, services it provides, capabilities it has. If the internal environment becomes weak for an organization, it will also lead to the downfall of the organization. Organizations those do not develop capabilities continually or stop innovating or their culture becomes toxic, will for sure lead to organization’s failure.
4. Strategies
(Innovation, Cost leadership, Quality, Focus, Customer intimacy)
Based on the organizational vision, goal, objectives, understanding of the external and internal environments, the organization must develop suitable strategies to be successful in the marketplace. Common strategies that most organizations follow are innovation, cost, leadership, quality, focus, and customer intimacy. There can be multiple strategies playing together in the organization.
However, the organization must figure out what strategy works well for the given size and maturity of the organization and act accordingly. Strategy affects organizational operations as well as sets the direction for the organization. One must be very careful in choosing strategy but at the same time, not get paranoid regarding it. This is because the strategies may work or may not, and one must figure out and adjust the organization strategy as it moves forward in the organizational journey.
5. Customer management
(Segments, value propositions)
Though customers are stakeholders as well, we must differentiate them as they are the most valuable stakeholder in the organization. Customers are the only source of revenue for any organization and understanding customer needs is extremely vital for any organization to be successful. The organization should identify the different kinds of segments and then develop propositions of the right value, which will attract potential customers to the organization. At the same time, the organization also must understand profitability aspects for each of the customer segments and figure out a way to serve each customer segment profitably.
6. Cost management
(Structure, Optimization)
If costs are not managed well in an organization, it will lead to a drop in the profitability and finally leading to shutdown of the organization. As business analysts, we should understand the different elements of the cost structure, and which elements of the structure can be optimized for organizational benefit. At the same time, one must be careful that the lowest cost is not necessarily the optimized cost because the lowest cost could compromise on the product or service quality. This, in turn, would affect organization’s customer satisfaction and ability to earn revenue from its customers.
7. Stakeholder management
(Identification, Analysis, Engagement)
Business analysts need to understand stakeholders for the organization, initiative or project as everything that business analysts do must add value to the stakeholders. Effective stakeholder management is essential for the success of any change. Stakeholders could be internal or external to the organization.
Key steps that we would follow for stakeholder management would be to identify stakeholders, analyze stakeholders for the criticality and contribution. Of course, business analysts must engage with stakeholders to reap benefits from the initiative.
8. Product and services management
(Portfolio, Contribution, Improvement, Processes)
Next element that we business analysts need to understand is product and services of the organization. Most organizations offer multiple products and services. It is essential for the organizations to understand the portfolio that they would like to maintain, contributions coming from different product and service lines, what kind of improvements or innovations are possible in existing products and services, and to develop new products and services, and bring about improvements to the processes carried out in the organizations.
9. Risk management
(Identification, Analysis, Mitigation)
Any organization has multiple risks from different sources including external and internal sources. Organizations must be cognizant of the sources of risks that it faces and develop suitable mitigations for managing business risks. Some activities can put the organization at a serious loss (even leading to the closure of the organization). All of us know the story of Enron and Arthur Andersen when they violated government regulations and finally leading to the closure of both these organizations. Not understanding risks coming from technological or demographic changes of customers can lead to companies going bankrupt because their products no longer have demand in the marketplace.
10. Resource management
(People, Financial, Technological, Physical)
The last element we discuss is resource management. Resources are essential for delivering any product and services to customers. Different kinds of resources that the organization must develop, maintain, and improve include people resources, financial resources, technological resources, and physical resources.
Nature of resources that an organization should possess is changing dramatically over the time. For many services organization in the olden days, having physical assets was very helpful. Today, in certain segments, it’s probably better not to have physical assets, but rather have digital assets. Physical assets require a significant amount of money to be maintained. In future, organizations will develop more and more digital assets as maintaining digital assets cost less, and can earn revenue across the globe, whereas physical resources mostly earn revenue from a specific geography.