Maximizing Business Analysis with ITIL: A Strategic Integration for Success
In the dynamic landscape of modern business, the role of a Business Analyst (BA) stands as a linchpin between technological advancements and strategic objectives. Within this realm, the integration of ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) principles has emerged as a pivotal force, reshaping the way BAs navigate and optimize business processes.
Understanding ITIL:
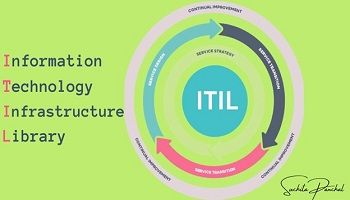
At its core, ITIL represents a comprehensive framework that encapsulates a set of best practices for IT service management. ITIL has evolved into a globally recognized framework, offering guidance on aligning IT services with the needs of the business. It comprises a collection of detailed practices, emphasizing service lifecycle management, continual improvement, and customer-centricity.
Enhancing Business Analysis with ITIL:
For Business Analysts, the incorporation of ITIL principles serves as a catalyst for profound change, fostering a more strategic and holistic approach to their responsibilities. Let’s explore how ITIL augments the role of a BA:
- Structured Process Analysis: ITIL provides a structured framework for analyzing, designing, and improving processes. BAs leverage this methodology to gain a comprehensive understanding of IT service lifecycles, enabling them to streamline operations and enhance efficiency.
- Facilitating Effective Communication: With a standardized language and terminology, ITIL bridges the communication gap between IT teams and business stakeholders. BAs proficient in ITIL can effectively convey complex technical concepts in a language that resonates with organizational objectives.
- Informed Decision-Making: By embracing ITIL methodologies, BAs gain insights into service strategy, design, transition, and operation. This knowledge equips them to make informed decisions that align IT services with overarching business goals.
- Continuous Improvement Culture: The core principle of continual service improvement in ITIL aligns seamlessly with the BA’s pursuit of optimizing business processes. BAs facilitate a culture of ongoing enhancement and adaptation, ensuring that IT services evolve in tandem with organizational needs.
- Risk Mitigation and Adaptability with: ITIL equips BAs with the tools to anticipate and mitigate risks effectively. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions, ensuring business continuity in the face of technological or operational challenges.
Advertisement
Real-world Impact and Success Stories:
Numerous success stories attest to the transformative impact of integrating ITIL into the scope of Business Analysis. Organizations have witnessed improved service delivery, increased operational efficiency, and a more strategic alignment between IT initiatives and business objectives. BAs proficient in ITIL frameworks have played a pivotal role in orchestrating these successes, driving innovation, and fostering a collaborative environment that embraces change.
Challenges and Adoption:
While the benefits of ITIL integration are substantial, challenges in implementation persist. Resistance to change, organizational inertia, and the complexity of aligning ITIL methodologies with existing processes often pose hurdles. BAs navigating this landscape must demonstrate strong leadership, communication skills, and a keen understanding of organizational dynamics to facilitate successful integration.
Continuous Learning and Evolution:
In the ever-evolving realm of technology and business, the journey of a BA integrating ITIL principles is an ongoing process. Continuous learning, staying abreast of updated ITIL practices, and adapting to changing business landscapes are essential for sustainable success.
Conclusion:
ITIL isn’t merely a set of guidelines for IT management; it’s a strategic enabler for Business Analysts. Its integration empowers BAs to be strategic partners, driving organizational success by aligning IT initiatives with business objectives, fostering innovation, and enabling a culture of continual improvement. Embracing ITIL principles expands the horizons of Business Analysis, transforming it into a proactive and value-driven function crucial for the modern enterprise.
The synergy between ITIL and Business Analysis isn’t just a trend; it’s a strategic imperative for organizations seeking to thrive in an increasingly digital and competitive landscape.