Several schools of thought have proffered reasons why projects fail; notable amongst these are studies by Forbes, the British Computer Society, Gartner, and many others. Generally, the causes of IT project failures have been described as ranging from poor business cases, requirements management, project management, talent, and poor processes.
Conversely, certain factors, which are described below, can be identified as factors responsible for successful projects.
BA competencies are a set of knowledge, behaviour, attitudes, and skills that enable a business analyst to perform business analysis successfully and efficiently. These BA competencies can be mapped to the factors that guide the successful delivery of IT projects.
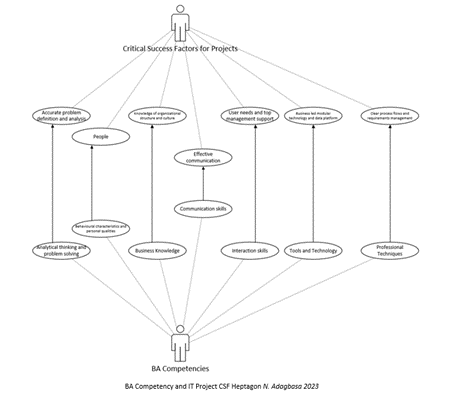
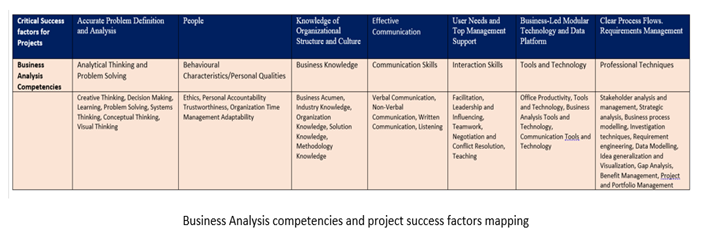
Accurate problem definition and analysis
This is central to delivering successful projects as it entails proper identification of problems, the scope, and thoughts around solutions. One major reason for IT project failure is that the business is often focused on the consequences or symptoms of an underlying problem and quickly directs technology to resolve these symptoms. At best, the result is an expensive IT solution that is sparsely used by the users, who often find workarounds or, at worst, IT projects that fail.
BA Competency: Analytical Thinking and Problem Solving
This competency employs critical thinking, system thinking, and problem-solving techniques, amongst many others, to help carry out root-cause analysis and produce problem statements that help correctly identify a problem.
People
People are an organisation’s greatest asset. Several schools of thought, including Herzberg’s, Maslow’s, etc., have carried out studies on employee productivity. Too often, while embarking on IT projects, the focus is on the technical skills of the project team, while knowledge around behavioural attributes, emotional intelligence, and concepts that affect productivity resides with the human resources team, who are seldom part of the IT project team.
BA Competency: Behavioural Characteristics and Personal Quality
BAs understand behavioural characteristics and human resources concepts of motivation, productivity, and emotional intelligence and constantly need to keep these in sight as they seek to understand the problem and define relevant requirements for a successful solution.
Knowledge of organizational structure and culture
While structure deals with norms, rules, and policies, culture is concerned with organisational values, behaviours, and attitudes, and both can affect the agility of project delivery. Thus, an optimal combination of the two is vital to successful project delivery.
BA Competency: Business Knowledge
This involves the application of business acumen, industry, organisation, appropriate methodology, and solution knowledge. Peter Drucker famously declared that culture eats strategy for breakfast, buttressing the importance of a thorough understanding of business to aid organizational success.
Effective Communication
This is the process of exchanging ideas, thoughts, opinions, knowledge, and data so that the message is received and understood with clarity and purpose. The challenge for many businesses is that this is not recognised as a skill that goes beyond writing and speaking. It involves non-verbal communications, listening, and analysis. When this is lacking in an IT project, the risk of failure is increased.
BA Competency: Communication Skills
Business analysts act as intermediaries between the business and IT and, as such, are trained in effective communication skills. They understand business and IT concepts and help to facilitate and interpret conversations to help all stakeholders deliver successful solutions.
Advertisement
User needs and top management support.
IT solutions are intended to meet user needs; however, a major reason for IT project failures is half-hearted support from top management. Often, top management is concerned with strategy and has a broad view of concurrent projects without knowledge of user needs. There is therefore a disconnect between project delivery and top management, with the resultant effect that projects don’t get the full backing required for success. Support is usually given in principle but lacking in practice as top management is often far removed from the projects.
BA Competency: Interaction Skills
Business analysts not only act as the intermediary between IT and the business but can also act as an intermediary between top management and the business. With their interaction skills, they can drive conversations among stakeholders and ensure that difficult questions are asked and resolved to ensure the successful delivery of projects.
Business-Led Modular Technology and Data Platform
Organizations that intend to deliver successful IT projects need to have a modern technology architecture driven by business needs, as evidenced by data. Advances in technology mean that businesses no longer have the choice of being either technology-savvy or operating on the fringes of the technology spectrum. Technology drives agility in today’s business environment, and the influx of AI makes it more expedient that businesses that want to thrive will need to invest in sound technology architectures and platforms.
BA Competency: Tools and Technology
This BA competency fosters the knowledge and use of tools and technology to drive productivity. From the use of general communication and office productivity tools like ‘Teams, Slack, etc. to business analysis tools like Jira, Azure, Visio, etc. to AI tools like Chat-GPT, Google Bard, Slides AI, etc., business analysts are equipped to be versatile while continuing to broaden their toolset.
Clear Process Flows and Business Requirements Management
This covers the end-to-end process of delivering an IT project; it encompasses identifying the right requirements, managing stakeholders, ensuring an accurate depiction of information flow through the organisation, and managing change.
BA Competency: Professional Techniques
This deals with delivering excellence by design. It is an aggregation of several BA competencies with a focus on ensuring that excellence is delivered at every point of the customer journey. This implies understanding an organisation in terms of its people, processes, steps, and the data required to make each step as efficient as possible.
Concluding Remarks
Historically, the rate of IT project failures has been high; however, opportunities now abound to turn the tide. As knowledge and awareness continue to increase and the business analysis skillset becomes more mainstreamed across organisations, there is an opportunity for business analysts to hone their craft, be more visible, and help stem the tide.